Disclaimer: Mladysrecords. This site provides fashion and lifestyle content for informational purposes only.
Did you know that approximately 20 million Americans suffer from thyroid problems? Statistics show that more than three out of five individuals with thyroid disease are unaware of their condition. Almost two percent of the population have been diagnosed with hypothyroidism worldwide. Due to the rising number of patients diagnosed with hypothyroidism in Provo, visiting an endocrinologist at the earliest sign of disease is crucial.
Hypothyroidism is a disorder in which the thyroid gland does not adequately produce enough hormones, leading to impaired metabolism. As such, people with this condition may experience symptoms reflecting their slowed metabolic rate.
Around 20 million Americans struggle with some form of thyroid disorder, which is expected to continue rising. Even more dauntingly, nearly 60 percent of those with this ailment remain unaware of their diagnosis. Unsurprisingly, women are five to eight times as likely as men to be affected by this health issue. The current estimation suggests that in the U.S., approximately 12 percent will experience a thyroid condition at least once during their lifetime!
The early diagnosis and treatment of hypothyroidism are essential as they can help minimize the symptoms and improve overall health. You should also follow some health and wellness tips to help manage hypothyroidism.
What Is Hypothyroidism?
Hypothyroidism is a condition characterized by abnormal thyroid gland function, which is responsible for the production of hormones responsible for metabolism. Since women have an eight-fold risk of developing hypothyroidism, endocrinologists strongly emphasize the importance of regular laboratory workup, especially among females with familial predisposition. Gradual thyroid inactivity may occur due to several conditions that destroy the individual function of your thyroid cells.
What Causes Hypothyroidism?
The most common cause of hypothyroidism is autoimmune thyroiditis, which is a condition wherein your own immune cells mistakenly attack normal thyroid cells. Since the immune system is activated upon detection of foreign bodies, functional thyroid cells are normally preserved in a healthy individual. However, in some people, heightened immune function may cause self-destruction of normal thyroid cells. This leads to inflammation and subsequent destruction of the thyroid gland.
Another common cause of hypothyroidism is external surgical or medical management that has altered normal thyroid development. Radioactive iodine (RAI) is the mainstay of treatment in most cases of hyperfunctioning thyroid. Therefore, if an individual undergoes RAI treatment, he may experience rebound hypothyroidism due to the adverse effect of radiation. Surgical intervention may also cause a significant decline in thyroid hormone levels. Since surgical removal is the mainstay of treatment in thyroid malignancy, removal of this gland may cause an abrupt decrease in thyroid hormone.
What Are the Symptoms of Hypothyroidism?
 Thyroid hormone plays a major role in regulating the metabolic function of all organs in the body. Hence, hypothyroidism has significant effects on all the major organs of the body. Common clinical manifestations include excessive fatigue, weakness, irritability, and memory loss. You may also experience constipation, weight gain, skin dryness, and hair loss due to impaired metabolic function.
Thyroid hormone plays a major role in regulating the metabolic function of all organs in the body. Hence, hypothyroidism has significant effects on all the major organs of the body. Common clinical manifestations include excessive fatigue, weakness, irritability, and memory loss. You may also experience constipation, weight gain, skin dryness, and hair loss due to impaired metabolic function.
How Is Hypothyroidism Treated?
Hypothyroidism can be detected through examination by a physician and subsequent laboratory testing. Measurement of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), free T3 (FT3), and free T4 (FT4) may be done to determine if the patient’s clinical picture correlates with the laboratory results. Ultrasound of the neck and thyroid may also be done to check for nodules that alter thyroid hormone levels. Once the diagnosis is confirmed, supplementation through medication intake is done to treat the inactive thyroid gland and restore normal hormone levels.
Hypothyroidism is a disease that results in impairment in growth, metabolism, bone development, and energy use. Since most thyroid disorders respond to medical or surgical treatment, endocrinologists strongly recommend early testing to ensure an accurate diagnosis. Therefore, it is crucial to visit an endocrinologist for further workup to ensure immediate management of the disease.
Diagnosis of Hypothyroidism
To diagnose hypothyroidism, your doctor must take a medical history and complete a physical exam. Characteristic symptoms of the disease are not exclusive to it alone, as they can also indicate other illnesses.
Blood Tests
That’s why several blood tests for thyroid hormones and imaging examinations may be necessary to determine and identify its cause accurately. Diagnosis of hypothyroidism primarily occurs through the thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) blood test. Depending on your symptoms and other factors, a healthcare provider may order additional tests to determine if conditions like Hashimoto’s disease are present.
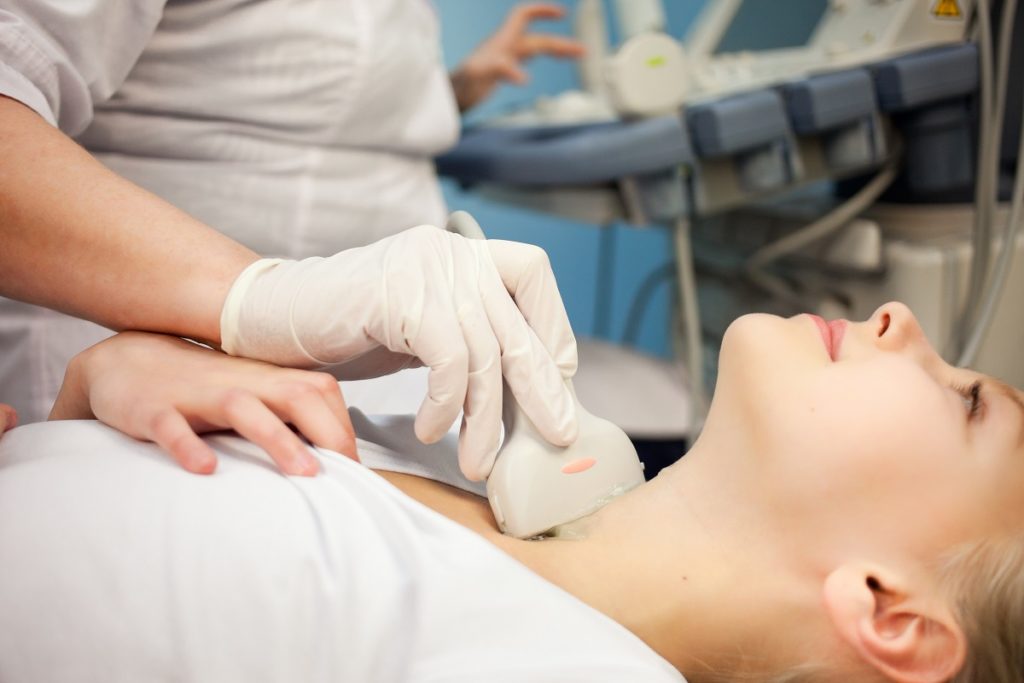
Ultrasonography
Ultrasonography is also essential for diagnosing nodular thyroid disease, and utilizing standardized imaging techniques and reporting formats will ensure that patients receive the best management strategies possible. Technology is integral in providing accurate diagnoses of this condition so that appropriate treatment options can be offered to those affected.
Management of Hypothyroidism
With the proper care and medication, hypothyroidism can be managed. Continuous use of your prescribed drugs will ensure that hormone levels in your body remain consistent throughout life. Regular visits with a healthcare provider to monitor progress will make you live just as healthy and normal of a life as anyone else!
Medication
Levothyroxine, an identical thyroid hormone to what is naturally produced by a healthy gland, will be prescribed as pills. You may also find it as liquid or soft gel capsules if you have issues with digestion and need extra help absorbing the medication. For best results, your doctor may advise taking this medicine in the morning before breakfast.
Dietary Changes
Making dietary changes can also help manage hypothyroidism. Your doctor may advise increasing foods rich in iodine, selenium, and zinc to support healthy thyroid functioning. Eating plenty of high-fiber foods like whole grains, beans, and legumes can also help keep your digestion regular and balanced. Additionally, you should avoid foods high in saturated fats and processed sugars, as these can worsen symptoms.
For those with hypothyroidism, weight gain can be an unfortunate side effect of slowed metabolism. However, following a nutritious diet may allow you to achieve weight loss in 3 months or less. The diet will enable you to manage your weight and contribute to your overall well-being. In addition, a person may notice a slight weight reduction — typically under 10 percent — when they take medication to treat hypothyroidism.
Exercise Regimen
In addition to medication and dietary changes, an exercise regimen is essential for managing hypothyroidism. Exercise helps reduce stress levels and increases the release of endorphins, resulting in improved moods and sleep cycles. High-intensity exercise is the best way to burn calories, while low-intensity exercises can help tone and strengthen muscles. Finding an activity you enjoy, such as swimming or cycling, can also make it easier to stay committed.
Regular Medical Consultation
Finally, staying in contact with your healthcare provider for regular checkups and follow-up appointments is crucial. Your doctor can provide personalized advice on how to manage your hypothyroidism best and suggest lifestyle changes or treatments that may be beneficial. This is particularly true for senior adults who have the condition. The healthcare provider can provide a list of healthy habits for elders to follow.
Hypothyroidism Treatment Methods
For the most common treatment of hypothyroidism, daily thyroid hormone replacement medication is carefully prescribed. Unfortunately, medicines can have unwanted side effects, and missing a single pill could result in further symptoms.
Combination Therapy with Levothyroxine and Liothyronine
Conventional treatment for hypothyroidism commonly involves levothyroxine monotherapy, though some patients still experience symptoms related to thyroid hormone deficiency. As such, there have been proposals that a combined regimen of liothyronine and levothyroxine may be more beneficial in achieving results.
Natural Remedies
If you’re looking to treat the root cause of your thyroid condition, natural remedies or alternative medicine may suit you. Poor diet, stress, and missing nutrients are often the source of a malfunctioning thyroid. Taking an herbal supplement could help address this issue with fewer side effects than medication alone would provide. Adjusting one’s diet is also highly recommended, as it can help alleviate many symptoms of low or underactive thyroids.
Dietary Changes to Increase the Iodine Intake
Eating the right foods can help manage your hypothyroidism symptoms. Incorporate these healthy options into your diet: non-starchy and starchy vegetables, fruits, fish, eggs, healthy fats, and gluten-free grains. Your diet may include seeds, nuts, beans, and beverages like herbal teas to keep you hydrated. At this point, you are now ready to start thriving with hypothyroidism!
Acupuncture and Yoga
Acupuncture can be an effective therapy for treating thyroid issues, as it has the potential to harmonize hormones and energy levels, soothe emotions and improve sleep patterns. Specific acupuncture points on the body have been proven to optimize the production of thyroid hormones. Treatments factor in your individual needs and consider all signs and symptoms, ultimately aiming to restore equilibrium within the body for enhanced wellness.
Evidence suggests that stress may be linked to hypothyroidism, yet yoga poses help stabilize thyroids, whether overactive or underactive. Multiple studies have demonstrated the advantages of incorporating yoga in improving thyroid functioning. Remember that these positions can’t replace any treatments or medications you might already be using!
Hypothyroidism is a serious health issue affecting millions of Americans and can be managed properly. Early diagnosis and lifestyle changes like diet, exercise, and natural remedies are essential for managing this condition. Furthermore, medication such as levothyroxine or liothyronine may help restore normal hormone levels. While finding what works best for you may take time and patience, it’s important to remember that there is hope – hypothyroidism doesn’t have to define your life! With dedication and perseverance toward following a healthy routine tailored specifically for you, living symptom-free will become an achievable goal.
Frequently Asked Questions
1) What causes hypothyroidism in pregnancy?
Pregnancy-related hypothyroidism, or gestational hypothyroidism, is caused by the changes in your hormones due to pregnancy. It usually occurs when the thyroid gland fails to produce enough hormones needed for normal body functions.
2) Does birth control affect the thyroid?
Birth control pills may affect the levels of hormones in the body and can, therefore, affect thyroid function. It is important to discuss potential side effects with your doctor before taking any medications.
3) Can hypothyroidism cause erectile dysfunction?
Hypothyroidism can cause erectile dysfunction as it affects the production of hormones in the body. Low testosterone levels, caused by hypothyroidism, can lead to decreased libido and difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection.
4) Will hypothyroidism make me gain weight?
Hypothyroidism can cause weight gain, affecting how the body processes carbohydrates and fat. Eating a balanced diet and regular exercise are essential steps to help manage your weight while living with hypothyroidism.
5) Are there any foods to eat to treat hypothyroidism?
Foods rich in iodine, selenium, and zinc can help support healthy thyroid functioning. Adding high-fiber foods such as whole grains, beans, and legumes can help keep digestion regular.
6) What happens if hypothyroidism is not treated?
If left untreated, hypothyroidism can lead to complications such as heart disease, infertility, and depression. Working with your healthcare provider to ensure you receive the best possible treatment for your condition is essential.